It’s now a far too familiar scenario. When we speak to safety professionals considering deploying AI Vision, they aren’t sure where to get started with improving workplace safety. Often, even those who are vastly experienced and trained aren’t even sure what questions they should be asking. After all, with any innovation or technology, the perceived complexity can be confusing at the outset.

AI Vision is no longer an abstract concept reserved for research labs. Today, it’s transforming frontline safety in workplaces around the globe. In our conversations with safety leaders and clients, and across several webinars on AI Vision for workplace safety programs, we have seen some telling trends emerging. Our team has fielded hundreds of questions from safety directors, operations managers, and C-suite executives, all focused on improving safety.
Whether speaking with construction firms managing multi-site projects or manufacturing leaders overseeing complex production lines, the same topics surface repeatedly. In this blog, we explore the key questions and concerns safety leaders pose.
Three core areas of workplace safety concern for Executives
We have found that safety professionals share similar operational challenges and accountability pressures. Understanding these patterns reveals how effective safety leaders deploying AI Vision address fundamental business needs beyond just simple accident prevention.
Cultural and organizational impact for safety professionals
The most sophisticated question we encounter isn’t about technology: it’s about people and culture. Safety leaders consistently ask how AI Vision affects safety practices, workforce dynamics, skill development, safety initiatives, and organizational culture. This concern reflects a deeper understanding that successful safety technology must enhance human capability rather than replace it.
Organizations implementing AI Vision report that workers might initially express scepticism, particularly in unionized environments where automation historically meant job displacement. However, practical deployment reveals a different dynamic. AI Vision functions as an early warning system that empowers effective safety leadership. This allows frontline supervisors and safety professionals to intervene before incidents occur.
If we consider the data from real implementations, traditional workplace safety relies on periodic inspections and post-incident analysis. A safety manager might conduct PPE compliance checks twice per shift, capturing perhaps 5% of actual work time. AI Vision provides continuous monitoring, identifying non-compliance incidents that would otherwise go undetected until an accident occurs.
The business impact extends beyond compliance. When workers understand that AI Vision detects hazards they might miss (from equipment malfunctions to environmental changes, and blind spot dangers), they view the technology as protective rather than punitive. This shift in perception directly correlates with improved safety culture metrics, continuous improvement, and voluntary incident reporting. In short, safe work and improved safety and health for all.
Organizations report that AI Vision integration actually improves safety management and increases safety performance. Workers become more conscious of safe behaviors and safety protocols when they understand that the system provides real-time feedback. Rather than creating dependency, this awareness reinforces positive behaviors and builds stronger safety habits.

Quantifiable business value and ROI
The second category of questions focuses on measurable outcomes. Finance teams want concrete ROI projections, operations leaders need productivity impact assessments, and safety directors and effective leaders require compliance improvement metrics.
According to OSHA data, workplace injuries cost U.S. employers approximately $170 billion annually, with the average workplace injury carrying a $40,000 direct cost. Serious incidents escalate to $150,000 or more when accounting for regulatory fines, insurance adjustments, legal expenses, and operational downtime. In process industries where production interruptions can cost $100,000 per hour, preventing even one major incident creates considerable value.
Real-world deployment data support these projections. Organizations implementing AI Vision typically see benefits across the five categories outlined here.
1. PPE compliance
Baseline compliance rates average 75% across industries. AI Vision deployments consistently achieve 95%+ compliance within 90 days. This improvement directly correlates with reduced injury rates from inadequate protection.
2. Near-miss detection
Traditional reporting captures approximately 20% of actual near-miss events. Workers either don’t recognize incidents as reportable or lack convenient reporting mechanisms. AI Vision automatically identifies and logs these events, increasing near-miss data by 300-400%. This enhanced visibility enables proactive hazard mitigation before accidents occur.
3. Incident reduction
Organizations report 30-50% decreases in recordable injuries within the first implementation year. More importantly, they see reductions in high-severity incidents that drive high costs and regulatory scrutiny.
4. Insurance impact
Progressive insurance providers offer premium reductions for companies deploying proactive safety technologies. These savings compound annually, creating ongoing operational benefits beyond direct injury prevention.
5. Productivity enhancement
By reducing safety-related work stoppages and investigation time, operations flow more efficiently. Workers spend less time on manual safety checks and documentation, focusing instead on value-generating activities.
The ROI timeline varies by industry and implementation scope, but most organizations achieve positive returns within just months. Companies with higher baseline injury rates or more expensive operational disruptions often see faster payback periods.
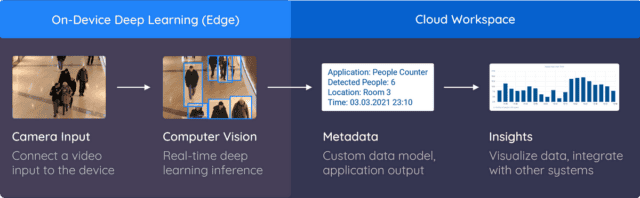
Data governance, privacy, and security
The third major concern addresses data handling, privacy protection, and regulatory compliance. These questions reflect growing organizational awareness of data governance requirements and worker privacy rights.
Modern AI Vision platforms address these concerns through a technical architecture designed for privacy preservation. Edge computing processes video streams locally rather than transmitting footage to external servers. This privacy-by-design approach ensures that sensitive visual data never leaves the facility while still enabling sophisticated AI analysis.
The system generates anonymized safety insights, such as “PPE violation detected, Zone 7” or “Forklift proximity alert, Dock 3”, without storing identifiable personal information. Workers cannot be individually tracked or monitored unless specific compliance or investigation requirements demand identification.
Organizations maintain complete control over data retention policies. Some facilities retain video for 30 days to support immediate incident investigation, while others keep data longer to support regulatory compliance or insurance requirements. Configurable retention ensures alignment with corporate policies and legal obligations.
GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific privacy regulations require explicit data handling protocols. AI Vision platforms provide strong safety, with detailed privacy controls, audit logs, and consent management to support compliance programs. Legal teams can review data flows, retention policies, and access controls to ensure regulatory alignment.
Transparency builds organizational trust. Companies successfully implementing AI Vision communicate openly about system capabilities, data handling practices, and privacy protections. When workers understand that AI Vision safety training enhances their safety without compromising their privacy, adoption proceeds smoothly.

Strategic implementation considerations
Beyond addressing immediate concerns, organizations evaluate AI Vision within broader operational contexts. These strategic questions reflect mature thinking about technology integration and long-term business impact.
1. Infrastructure integration
Most organizations ask about technical requirements and infrastructure costs. AI Vision typically leverages existing camera networks, minimizing upfront investment.
2. Change management
Successful implementations require structured change management programs. Organizations that invest in worker education, supervisor training, and clear communication see faster adoption and better outcomes than those treating AI Vision as purely a technical deployment.
3. Performance measurement
Leading organizations establish baseline safety metrics before implementation and track improvements systematically. Key performance indicators include injury rates, near-miss reporting, compliance scores, and worker feedback metrics.
4. Regulatory alignment
Different industries face varying regulatory requirements. AI Vision supports compliance with OSHA standards, industry-specific safety regulations, and corporate safety policies. Organizations use AI data to demonstrate proactive safety management during regulatory inspections.
5. Scalability planning
Multi-site organizations plan AI Vision deployment strategically, often starting with high-risk facilities or sites with existing safety challenges. Lessons learned from initial implementations inform broader rollout strategies.

Emerging applications and future considerations
Our discussions with safety leaders increasingly focus on advanced applications beyond traditional safety monitoring. At the outset, we see organizations typically explore AI Vision for the following applications.
1. Predictive safety analytics
Advanced implementations use AI Vision data to identify leading indicators of safety incidents. Patterns in near-misses, compliance trends, and environmental factors enable proactive intervention strategies.
2. Dynamic environment management
Construction sites, mining operations, and other changing environments benefit from AI systems that adapt to evolving conditions. Mobile applications complement fixed cameras, enabling safety monitoring in temporary or remote locations.
3. Cross-site learning
Organizations with multiple facilities use federated learning to improve AI models across sites without sharing sensitive video data. Best practices and hazard recognition capabilities developed at one location benefit the entire enterprise.
4. Vehicle and equipment safety
Fleet management applications detect driver fatigue, distraction, and risky behaviors. Integration with existing telematics systems maximizes infrastructure value while improving vehicle safety outcomes.
The questions safety leaders ask about AI Vision reflect fundamental business challenges: protecting workers, managing risk, demonstrating regulatory compliance, and optimizing operations. Organizations that approach AI Vision strategically, considering human factors, measuring business impact, and managing data responsibly, achieve the most significant safety and financial benefits for team members.
As AI Vision technology continues advancing and deployment experience grows, the questions will evolve. However, the core concerns about people, performance, and privacy will remain central to successful implementation strategies. Successful deployment of AI Vision emphasizes the importance of safety and accelerates the path to zero harm.
