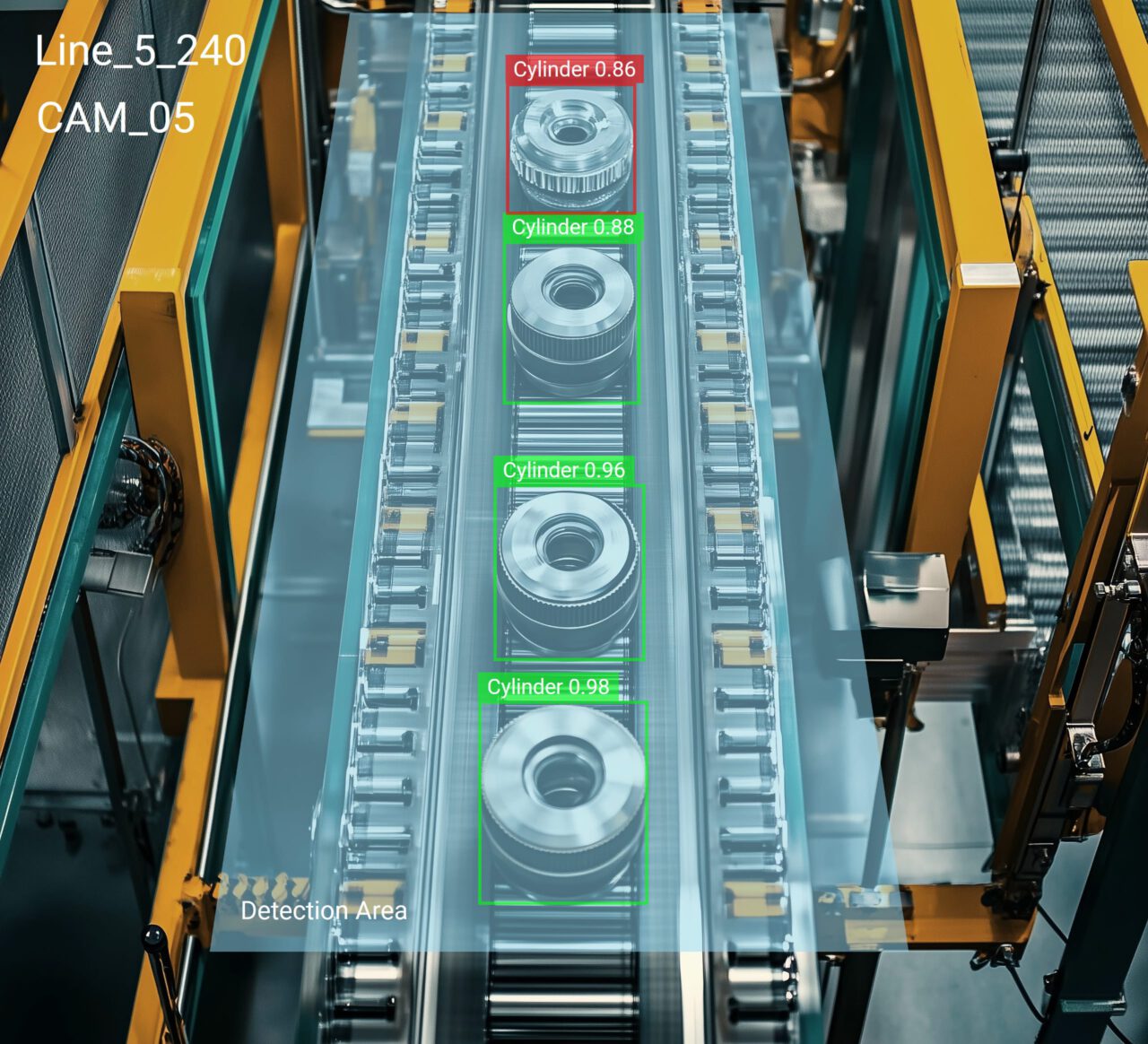
Computer Vision (CV) offers significant advancement in the manufacturing industry with its ability to ensure manufactured products meet quality standards and remove any defective products. At the same time, all this is being done with high precision and efficiency using CV in an assembly line.
To identify defective products during manufacturing, computer vision uses live video input from cameras installed. With the help of edge devices, the model detects any surface imperfections, assembly errors, or any other product inaccuracies in real time.
Why Assembly Lines Need Computer Vision
With intense competition in the manufacturing industry, it is crucial to make sure that products are of a high standard, any inadequate products result in a substantial loss in revenue and customer satisfaction, and as a result, there is no room for error.
Manual inspection by humans is prone to errors, especially when there are thousands of products that need inspection every hour. In contrast, CV offers accuracy and speed that are superior to any human inspection, even at a high volume of production.
- Computer vision applications detect the most minute defects with remarkable precision. A human inspector likely misses minute details that are invisible to the human eye.
- Automated CV applications can process visual data at exceptional speeds, inspecting hundreds or thousands of products per minute. To just match this speed of production, a large number of human inspectors are required, while at the same time, sacrificing accuracy.
- Unlike humans, CV applications are consistent at all times across all inspections. A human inspector introduces variations in accuracy that can arise from factors like fatigue or subjective judgment.
How Computer Vision Detects Defective Products
- Image Input: High-resolution cameras installed in the manufacturing area capture images of products on the assembly line.
- Feature Extraction: CV applications deploy advanced AI algorithms to analyze images and identify features that indicate defects. For example, models like Faster R-CNN are used for real-time object detection and defect classification.
- Real-time Analysis: Once that application is running, the model continuously monitors the assembly line. It processes each incoming image in real time. If a defect is identified, the system triggers automated responses, such as removing the defective item from the line or alerting human operators.
How a FMCG Manufacturer Implemented Computer Vision
One of the world’s largest fast-moving consumer goods manufacturers implemented a computer vision proof-of-concept system to detect defective products. The manufacturer needed a way to pull faulty toothbrushes from the assembly line before they were shipped out for distribution. The system implemented state-of-the-art computer vision models to detect defects, create alerts, and pull below-board products from the assembly line.
At the end of the project, the manufacturer calculated that if the system were rolled out on a large-scale basis just in the dental hygiene division, they would achieve more than $500 million annually. Thus, emphasizing the severity of sending faulty products to market.
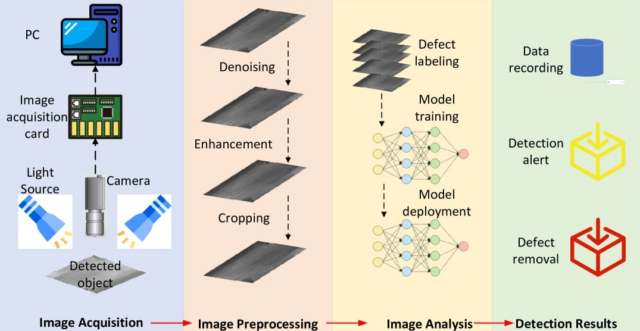
However, there are The ability to accurately identify defective products using a CV in an assembly line is used across industries:
- Automotive Industry: In the automotive sector, computer vision systems are used to inspect car components for defects such as surface imperfections, misalignments, and paint quality issues. This is crucial in meeting safety and quality standards before any vehicle reaches consumers.
- Electronics Manufacturing: CV is used to inspect printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electronic components. Detects such as minute soldering errors, component misplacements, and surface anomalies, are detected with high precision.
- Food and Beverage: In food processing, CV is used to detect any foreign objects, packaging defects, and labeling issues. This is important in ensuring hygiene standards and compliance with food safety regulations.
- Textiles and Apparel: In the textile industry, CVs in assembly lines are used to identify defects in fabrics, such as tears, stains, or color mismatches, helping with high-quality standards in clothing and also reducing waste production.
Business Value of Defect Detection
Incorporating a CV into any business results in enhanced profits, and sustainability thus increasing the chances for the business to thrive. Here is why:
- Operational Efficiency and Cost Reduction: CV automates processes that traditionally require human supervision, this leads to faster inspection times and reduced labor costs. As a result, businesses can achieve higher throughput with fewer resources, thus reducing operational expenses.
- Increased Product Quality: CV systems can consistently detect defects, errors, and substandard products in real time during the production process. This ensures that products delivered to customers are perfect. This increases the trust of customers in the company, positive outcomes, returning customers, and referrals.
- Competitive Advantage: Early adopters of computer vision technology can gain a first-mover advantage by improving their operational capabilities and product quality. This proactive approach positions companies as industry leaders and attracts tech-savvy consumers.
- Scalability and Flexibility: CV systems can easily scale to accommodate growing business needs without a proportional increase in labor costs. Additionally, this can be done instantly or at least, in a very short time. Making the business highly adaptable to increased demand.
- Sustainability and Environmental Impact: Businesses can contribute to sustainability efforts by reducing waste in the production process. This not only benefits the environment but can also enhance a company’s brand image as a socially responsible entity. Additionally, this can reduce business costs. Environmentally friendly businesses can qualify for various tax exemptions, credits, or incentives.
To learn more about implementing Viso Suite computer vision for intelligent defect detection and manufacturing automation, book a demo with our team of experts.