Depth analysis is an area of computer vision that involves estimating the distance between imaged objects and the camera. It allows for understanding a scene’s three-dimensional structure from two-dimensional data. Using artificial intelligence (AI), depth analysis allows machines to perceive the world more like humans. This empowers them to perform tasks like object detection, scene reconstruction, and navigating 3D space.
Putting Depth Sensing Into Context
Depth sensing technologies effectively began with the technique of stereo vision. These systems inferred distances by analyzing the differences between images taken from slightly different viewpoints. It works in a way that mimics human binocular vision.
The evolution continued with the structured light systems. This technique involves projecting a known pattern onto a scene and analyzing the distortions to calculate depth. Early models like the Microsoft Kinect are examples of this in action.
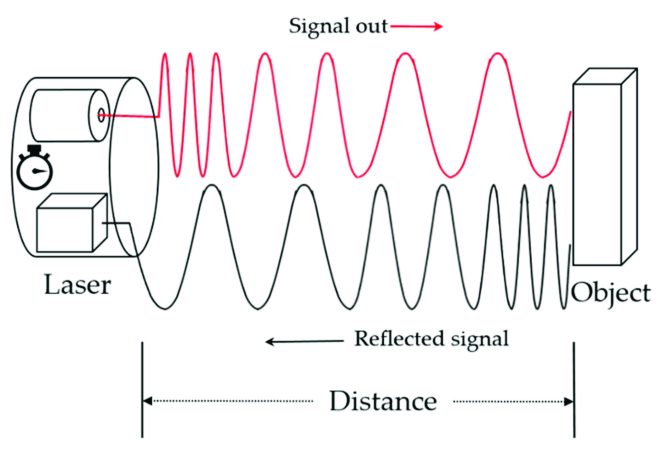
The introduction of Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors represented another breakthrough moment. These sensors measure the time it takes for emitted light to return, providing highly precise depth information.
In recent years, AI has revolutionized depth analysis by enabling monocular depth estimation—inferring depth from a single image. This was a significant leap forward, as it removed the need for specialized hardware. Other models have since set new standards for the accuracy and efficiency of in-depth prediction. This includes models such as MiDaS (Multi-scale Deep Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation) and DPT (Dense Prediction Transformers).
The introduction of large-scale datasets and advances in neural network architectures have further propelled this field. TikTok’s Depth Anything model is largely a culmination of all of these advancements.
Mastering depth analysis techniques opens up new possibilities in application development, from augmented reality to navigation systems. It can push solutions forward that satisfy the growing demand for intelligent, interactive systems.
Intro to TikTok’s Depth Anything
TikTok’s Depth Anything is a groundbreaking approach to monocular depth estimation. It effectively harnesses a combination of 1.5 million labeled images and over 62 million unlabeled images. This is a significant differentiation from traditional techniques, which primarily relied on smaller, labeled datasets. Leveraging the power of large-scale unlabeled data offers a more robust solution for understanding complex visual scenes.
Depth Anything has quickly become an integral component of TikTok’s technology ecosystem. It serves as the default depth processor for generative content platforms such as InstantID and InvokeAI. This is thanks to the model’s versatility and the enhanced user experience it offers through advanced depth-sensing functionalities. It also has applications in video depth visualization, which opens new avenues for content creation on TikTok’s platform.
Key Milestones in Development
- 2024-02-27: CVPR 2024 officially endorses Depth Anything.
- 2024-02-05: The release of Depth Anything Gallery, showcasing the model’s capabilities.
- 2024-02-02: Implementation as the default depth processor for InstantID and InvokeAI, enhancing platform functionalities.
- 2024-01-25: Introduction of support for video depth visualization, including an accessible online demo.
- 2024-01-23: Integration of a new ControlNet based on Depth Anything into ControlNet WebUI and ComfyUI’s ControlNet.
- 2024-01-23: Support for ONNX and TensorRT versions.
- 2024-01-22: Release of the Depth Anything paper, project page, code, models, and demonstrations across platforms like HuggingFace and OpenXLab.
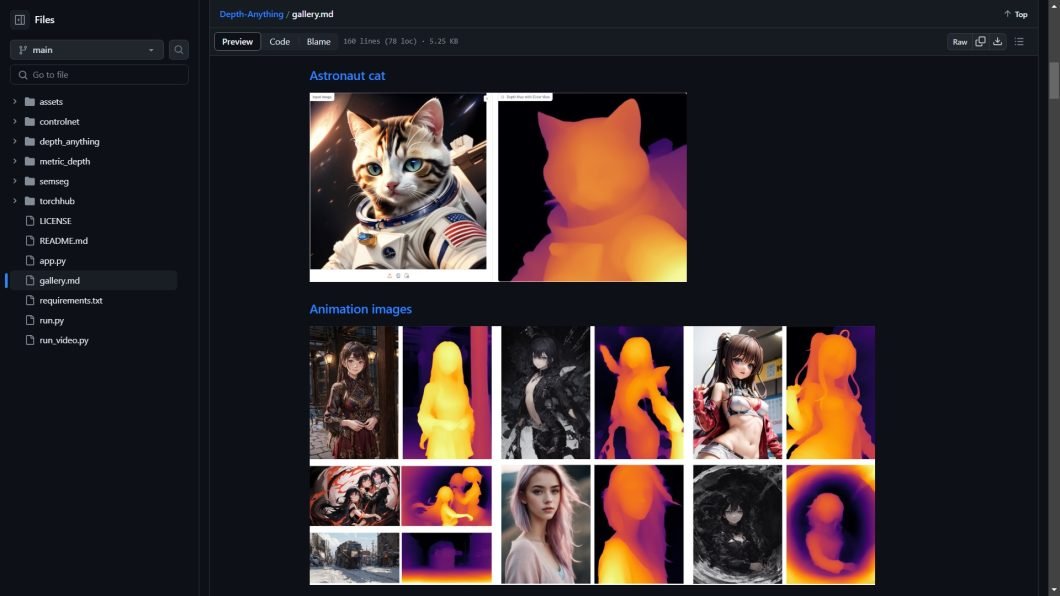
Depth Anything is an impressive model, performing exceptionally well compared to existing depth sensing techniques. Here are some of its key capabilities at this time:
- Improved zero-shot relative depth estimation over models like MiDaS v3.1 (BEiTL-512)
- Enhanced zero-shot metric depth estimation compared to models like ZoeDepth
- Optimal in-domain fine-tuning and evaluation on NYUv2 and KITTI
- Robust relative and metric depth estimation for any given image.
- Improved depth-conditioned ControlNet offering precise synthesis.
- Potential for downstream applications in high-level scene understanding tasks.
Depth Anything isn’t simply a core element of TikTok’s AI suite but also sets new standards for depth estimation.
Depth Analysis: A Technical Deep Dive
The key to Depth Anything’s architecture is ingeniously integrating both labeled and large-scale unlabeled data. The foundation model uses a transformer-based framework, bestowing it with the strengths of Vision Transformers (ViTs). This empowers it to capture complex spatial hierarchies and contextual information essential for accurate depth perception.
It also uniquely leverages the concept of inheriting rich semantic priors from pre-trained encoders. By integrating semantic priors, Depth Anything benefits from the vast, pre-existing knowledge encoded in these models. This approach allows the model to inherit a rich understanding of visual scenes.
Depth Anything also features a unique hybrid training approach. It uses a data engine to automate the annotation process for the vast corpus of unlabeled images it harnesses. A smaller, pre-trained model generates pseudo-depth labels for the images, seeking extra visual knowledge.
Then, it combines pseudo-labeled data with 1.5 million high-quality labeled images in a dual-path training mechanism. This setup incorporates both supervised learning for labeled data and semi-supervised learning for unlabeled data. This significantly enhances the model’s generalization capabilities across various scenes.
The training process involves a novel optimization strategy that adjusts the learning focus between labeled and pseudo-labeled data. For labeled images, it uses a standard regression loss function, such as Mean Squared Error (MSE). This minimizes the difference between predicted and actual depth values.
For unlabeled images, the model applies a consistency loss. This process encourages the model to produce similar depth predictions for slightly perturbed versions of the same image. It amplifies the model’s ability to interpret diverse visual scenarios while accurately deducing depth from subtle visual cues.
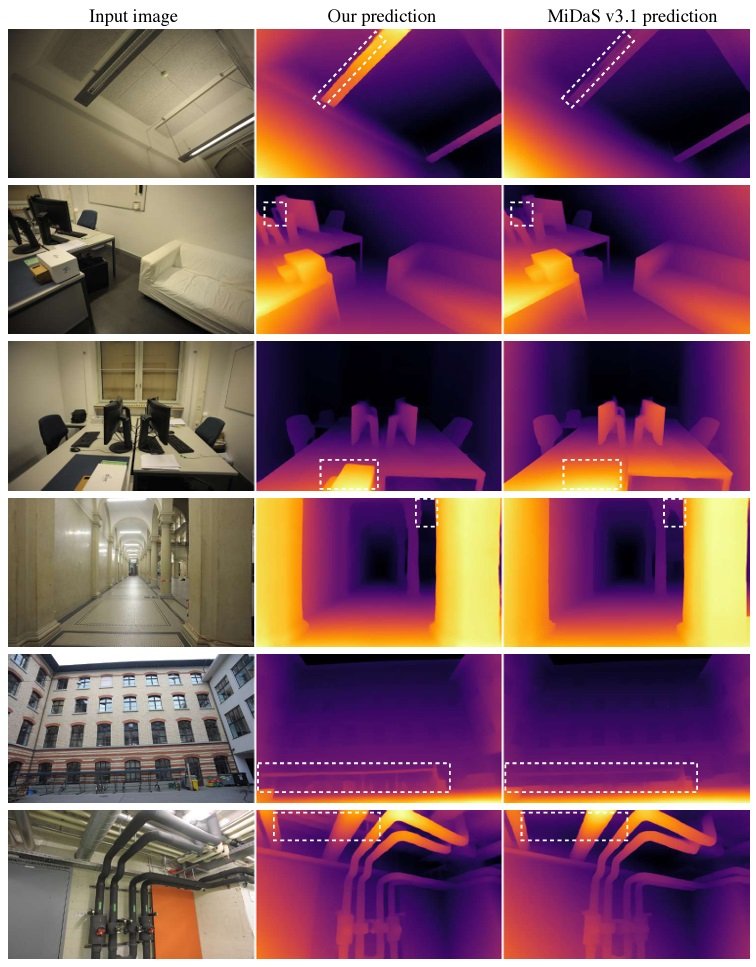
Key Technologies and Methodologies
- Relative and Metric Depth Estimation: Depth Anything leverages an adaptive binning strategy. It dynamically adjusts depth prediction ranges to optimize for both close and distant objects within the same scene. This approach is fine-tuned with benchmark metric depth information from NYUv2 and KITTI.
- Better Depth-Conditioned ControlNet: By re-training ControlNet with Depth Anything’s predictions, the model attains a higher precision in depth-conditioned synthesis. This is what allows Depth Anything to generate realistic and contextually accurate augmented reality (AR) content and virtual environments.
- High-Level Scene Understanding: Depth Anything’s encoder is fine-tuned for semantic segmentation tasks. Largely, thanks to using rich feature representations learned during depth estimation. It performs very well on scenes from Cityscapes and ADE20K proves its high-level capabilities.
A Performance Analysis of Depth Anything
The Depth Anything paper showcases this model’s marked advancements over the MiDaS v3.1 BEiTL-512 model. For this, it uses metrics like AbsRel (Absolute Relative Error) and δ1 (pixels with an error under 25%). A lower AbsRel and a higher δ1 score indicate improved depth estimation accuracy.
Comparative Analysis
According to these metrics, Depth Anything outperforms MiDaS v3.1 across various datasets:
| Dataset | Model | AbsRel ↓ | δ1 ↑ |
|---|---|---|---|
| KITTI | MiDaS v3.1 | 0.127 | 0.850 |
| Depth Anything (Small) | 0.080 | 0.936 | |
| Depth Anything (Base) | 0.080 | 0.939 | |
| Depth Anything (Large) | 0.076 | 0.947 | |
| NYUv2 | MiDaS v3.1 | 0.048 | 0.980 |
| Depth Anything (Small) | 0.053 | 0.972 | |
| Depth Anything (Base) | 0.046 | 0.979 | |
| Depth Anything (Large) | 0.043 | 0.981 | |
| Sintel | MiDaS v3.1 | 0.587 | 0.699 |
| Depth Anything (Small) | 0.464 | 0.739 | |
| Depth Anything (Base) | 0.432 | 0.756 | |
| Depth Anything (Large) | 0.458 | 0.760 |
Note: Lower AbsRel and higher δ1 values indicate better performance. The table demonstrates Depth Anything’s superiority across diverse environments.
Model Variants and Efficiency
Depth Anything can also cater to various computational and use case requirements. Therefore, it offers three model variants: Small, Base, and Large. Below is a table detailing their inference times across different hardware configurations:
| Model Variant | Parameters | V100 (ms) | A100 (ms) | RTX 4090 (TensorRT, ms) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 24.8M | 12 | 8 | 3 |
| Base | 97.5M | 13 | 9 | 6 |
| Large | 335.3M | 20 | 13 | 12 |
Note: This table presents inference information for a single forward pass, excluding pre- and post-processing stages. The RTX 4090 results include these stages when using TensorRT.
These results prove that Depth Anything is a highly accurate and versatile model that can adapt to various scenarios. It features state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets and computational efficiency across different hardware configurations.
Challenges and Limitations
One notable constraint of the model is its reliance on the quality and diversity of the training data. The model demonstrates remarkable performance across various datasets. However, its accuracy in environments vastly different from those in its training set can be inconsistent.
While its currency generalization is superb, it can be improved to better process images under any circumstances.
The balance between using unlabeled data for improving the model and the reliability of pseudo labels remains delicate. Future work could explore more sophisticated methods for pseudo-label verification and model training efficiency.
Another concern is that of data privacy, especially given the scale of unlabeled data. Ensuring that this vast dataset does not infringe on individual privacy rights requires meticulous data handling and anonymization protocols.
A final hurdle was the computational requirements to process over 62 million images. The model’s complex architecture and the sheer volume of data demanded substantial computational resources. This makes it a challenging optimization target to train and refine without access to high-performance computing facilities.
Applications and Implications
On social platforms like TikTok and YouTube, Depth Anything allows for unleashing the power of depth estimation or content creation. Creators now have access to advanced features such as 3D photo effects and interactive AR filters. Beyond social media, Depth Anything has the vast potential to impact many sectors.
For tools like InvokeAI, this means creating more lifelike and interactive AI-generated art. Depth information allows for nuanced manipulation of elements based on their perceived distance from the viewer. InstantID utilizes Depth Anything to improve identity verification processes. It improves security by enabling the system to better discern between a real person and a photo or video.
In AR experiences, precise depth estimation allows for the easy integration of digital objects into real-world scenes. This could greatly simplify complex scene construction tasks in gaming, education, and retail. For autonomous vehicles, the ability to accurately perceive and understand the 3D structure of the environment from monocular images can contribute to safer navigation.
In healthcare, similar technologies could transform telemedicine by enabling more accurate remote assessments of physical conditions.