Find the applications and most popular use cases of computer vision in manufacturing. We will cover real-world applications of how manufacturing companies can use deep learning and AI vision technologies to power Computer Vision for inspection, workplace safety, factory automation, and quality control.
In this article, we will provide a state-of-the-art overview, new ideas for computer vision projects, real-world examples, and an industry outlook.
1. Quality inspection with computer vision
One of the most important uses of computer vision in manufacturing is for automating quality inspection during the production process. Maintaining quality standards is of utmost importance in the field of manufacturing. While one can do this manually by engaging quality control experts, the chances of human error are quite high and naturally limited.
As a result, several manufacturing firms are shifting towards using deep learning and computer vision for quality control and inspection tasks. Adopting such technologies ensures minimal human intervention while maintaining a high level of accuracy in the process. Besides, these technologies are also economical, as they help improve operational efficiency and reduce labor costs.
In the restricted environment of a manufacturing plant, computer vision can perform many inspection tasks faster, more accurately, and efficiently than humans. It becomes possible to inspect every single part instead of just random samples.
Vision systems also apply a consistent standard to overcome variations across different human inspectors. Hence, an automated inspection can significantly improve the efficiency of consumer product manufacturing. For example, a hot sauce maker checks the placement of labels at a rate of over 1’000 per minute. Until now, machine vision inspection systems use methods that are custom-trained for particular inspection tasks and are unable to be retrained. However, machine learning-based approaches that are deep learning-based are much more flexible.

2. Optimizing supply chains
Optimizing the supply chain process is beneficial for manufacturing plants to reduce costs while enhancing customer satisfaction. While human intervention was necessary for overseeing several parts of the supply chain process in the past, advancements in the field of computer vision have brought a change in this aspect.
Several manufacturing enterprises have turned to computer vision applications for tasks like warehouse management, managing inventories, and improving efficiency in the organization. For example, companies like Amazon and Walmart are working to implement drone systems to monitor warehouse inventories. For example, real-time processing of camera streams is used to detect empty containers and optimize restocking.
3. Equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance
Manufacturing plants involve specialized equipment for the production of goods. With regular use, these machines may show signs of wear or even malfunction, leading to product defects and losses.
The use of computer vision technologies is much more effective than human observations in detecting such changes in manufacturing equipment. Such technologies have been used to recognize defects in real-time, even in tiny machine parts. This makes it possible to discover and repair the parts in time which could have otherwise caused the manufacturing process to slow down.
Deep learning is used for the fault diagnosis, leakage detection, and prognosis of industrial equipment. Machine learning techniques have been used to develop intelligent fault diagnosis systems. For example, deep learning has been used to find cracks in industrial components such as spherical tanks and pressure vessels in oil and gas applications.
4. Digital lean manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is a production process that attempts to maximize productivity while simultaneously minimizing waste within a manufacturing operation. Industry 4.0 technologies transform lean processes to advance the enterprise and provide a data-driven approach to decision-making and automation with intelligent sensing technologies. Computer Vision is a key component of Industry 4.0 technologies to digitize manufacturing plants.
Expert reports from Deloitte estimate that the transformation from lean to digital lean will generate improvement in EBITDA (earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization) of US$20 million yearly, decrease costs by 15% per line per year, and improve general equipment effectiveness (OEE) by 11% yearly.
For example, computer vision systems can recognize and track events and employee footfall (automated spaghetti diagram) to measure process efficiency, provide analytics to detect defective equipment and optimize workloads across the plant floor.
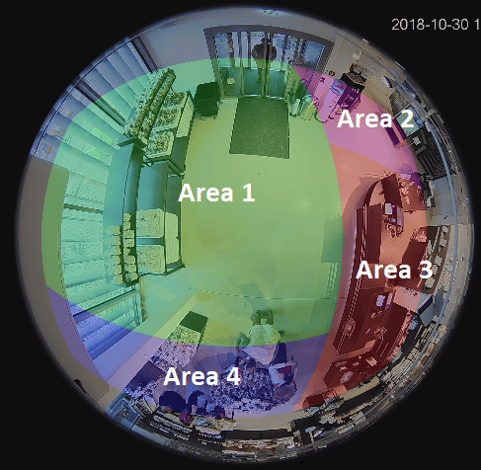
With the application of computer vision in manufacturing, it has become possible for many enterprises to embrace this strategy for enhancing their efficiency. The use of computer vision applications in different phases of the manufacturing process can help reduce time, wastage, and costs while simultaneously improving productivity.
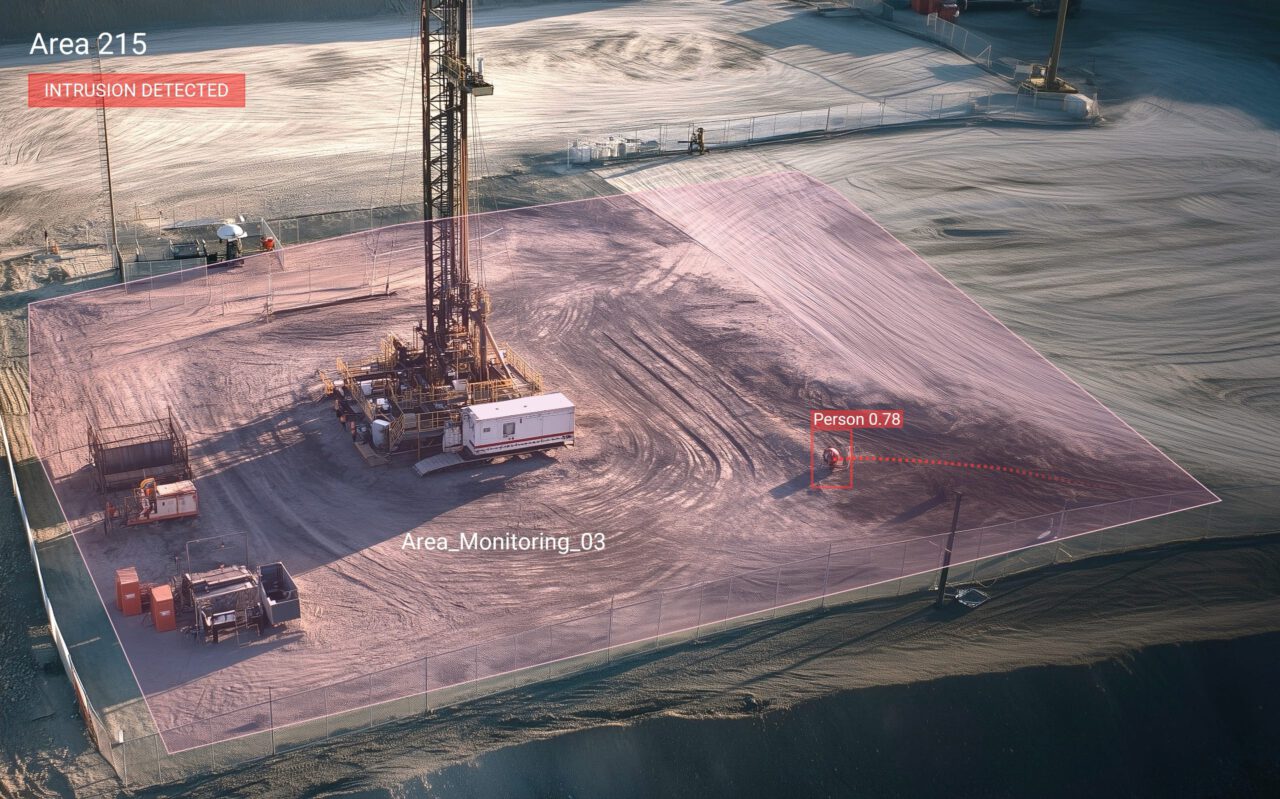
5. Safety of workforce and equipment
Workers in manufacturing enterprises often suffer injuries while on the job. For employers, ensuring the safety of their workforce is of immense importance as it directly affects production.
Manual monitoring processes are often insufficient as the appointed person may fail to effectively observe multiple screens at once. And such errors may have enormous consequences for the workforce and the manufacturing firm.
The use of computer vision technologies can effectively detect any issues related to safety measures for the workers to create reports in dashboards and send notifications. It is also possible to issue alerts automatically in case there is an accident so that the management can take the necessary measures immediately.
6. Detecting product defects
The use of computer vision in manufacturing can help detect defective products with remarkable ease. It can be tough to manually identify smaller defects in the products during the manufacturing process. Moreover, the delivery of an order containing a defective product can not only lead to increased production costs but also customer dissatisfaction.
Undoubtedly, this can have negative consequences for the business. Adopting a computer vision system for defect detection can save you from these troubles by efficiently monitoring the manufacturing process to identify defective pieces.
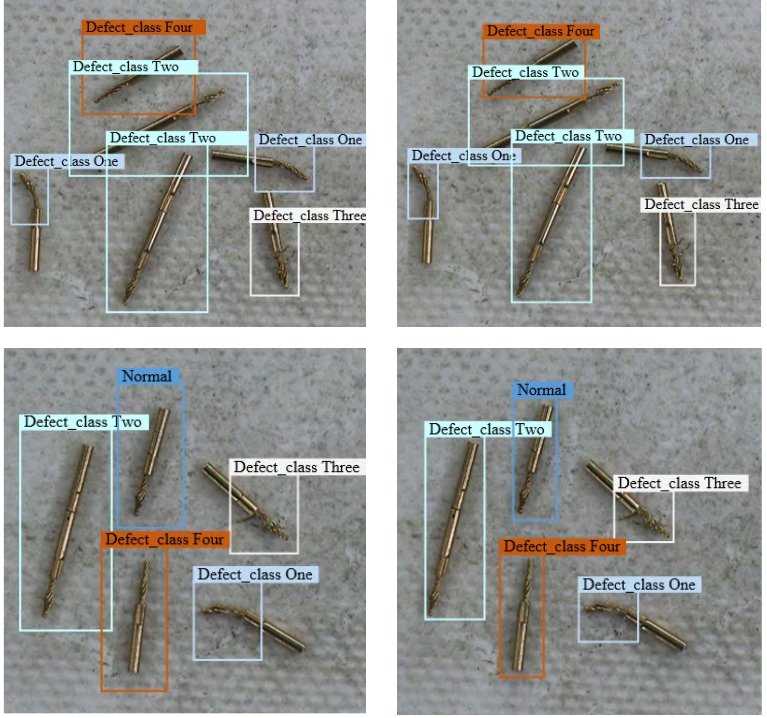
The example shows defect detection with a real-time deep learning system. It was tested with different AI algorithms, including YOLOv3 (32h training time), Faster-RCNN, FPN, and a single shot detector (SSD) neural network (98% accuracy rate). Compared to machine vision, deep learning is much more robust and flexible, making hardware comparably less costly.
7. Real-time Barcode Reading
Today, most products come with a barcode for easy identification purposes. Manufacturing firms need to ensure that the products have accurately printed barcodes before dispatching them to the market.
Manually verifying each barcode is a time-consuming affair, not to mention the associated costs of labor. Despite these manual checks, errors are inevitable. Computer vision systems are a preferable alternative here to recognize accurate barcodes. It can verify multiple barcodes in comparatively less time with high effectiveness.
Such systems can be trained to divert any product with faulty or incorrect barcodes to the manufacturing department for assessment.
8. Automated Product Assembly
Manufacturing firms all over the world are rapidly moving towards computer vision-based systems to automate their product assembly process. Along with ensuring accurate assemblage of the product, the use of computer vision makes the process much quicker.
This technology involves the generation of a 3D model design using specialized software based on which the computer vision system executes the process of assembly. This process is especially relevant for manufacturing plants dealing with small or delicate parts that cannot be properly managed by hand. The use of computer vision systems can precisely monitor and complete the assembly process with minimal error.
9. Maintaining Packaging Standards
Product packaging is of crucial importance for manufacturing firms as it helps protect the item from damage. To maintain their packaging standards, manufacturing firms often deploy computer vision-based systems.
The use of such technologies is particularly widespread in pharmaceutical computer vision applications, where it is essential to count the number of pieces before packaging. These manufacturers need to maintain a specified number of whole tablets or capsules per bottle without fail. Computer vision helps in doing the task with the required precision and automation.
Moreover, the system can be trained to check for damages on the final packaging and divert any product found lacking in this aspect. Another use case is the inspection of incoming goods to detect issues early and automatically document potential insurance cases.
10. COVID-19 Pandemic Protective Measures
As the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world in early 2020, it brought several manufacturing activities to a halt. Even as the activities resumed, several manufacturing plants made social distancing and wearing masks mandatory for workers’ safety.
Computer vision applications are tremendously helpful in this case, as they make it possible to effectively monitor the workforce to identify any violations of the Covid-19 protocol. In addition, the use of such computer vision models in manufacturing plants will ensure a safe working environment during and even after the pandemic.
Automated mask control was developed to detect unmasked people efficiently. Mask detection in factories is one of the most popular new use cases for computer vision.
Industry Outlook
Computer Vision has a wide range of applications in manufacturing, many of which have their origin in related industries. For example, person detection and tracking are already widely used in Retail applications. However, the efficiency gains of optimizing productions and automating safety systems often provide higher value compared to other use cases. We expect many more applications to be broadly introduced as deep learning technology matures, making it possible to power computer vision at scale.
New technologies such as Edge AI make it possible to scale AI vision systems with deep learning in real-world applications. The emerging new mega-trend is to move machine learning from the cloud to the edge to perform on-device processing with computers connected to cameras. Edge ML makes it possible to power high-performance, robust, and private computer vision applications.
What’s next
If you are interested in building and developing deep learning applications, check out Viso Suite, the end-to-end platform to build, deploy, and monitor computer vision applications in manufacturing.
Read more about related topics.
