Optical Character Recognition or Optical Character Reader (or OCR) describes the process of converting printed or handwritten text into a digital format with image processing. In this article, we’ll discuss
- What OCR is, and as well as how it works
- The best tools, algorithms, and techniques for OCR.
- The benefits of using OCR
- Use cases and OCR applications
Visual Text Recognition
Optical Character Recognition is a significant area of research in artificial intelligence, computer vision, pattern recognition, and machine learning. It was also one of the earliest fields of artificial technology research and has emerged as a mature technology.
It began back in 1913 when Dr. Edmund Fournier d’Albe invented the Optophone to scan and convert text into sound for visually impaired people. Since then, this technology has experienced multiple developmental phases.
In the 1990s, the technology became prominent with the digitization of historical newspapers. In addition, the emergence of smartphones and electronic documents has also led to further advancements in Optical Character Recognition(OCR) technology.
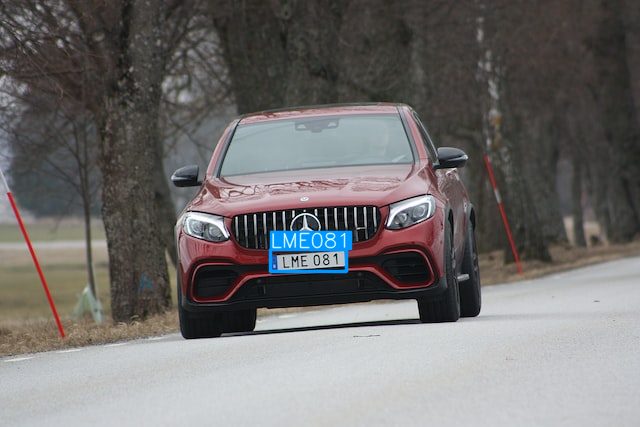

What is Optical Character Recognition (OCR)?
OCR stands for Optical Character Recognition and refers to a software technology that electronically identifies text (written or printed) inside an image file or physical document, such as a scanned document, and converts it into a machine-readable text form for data processing. We can also refer to it as “text recognition.”
In short, optical character recognition software helps convert images or physical documents into a searchable form. Examples of OCR engines are text extraction tools, PDF to .txt converters, and Google’s image search function.

What is Scene Text Recognition (STR)?
In computer vision, machines can read text in natural scenes by first detecting text regions, cropping those regions, and subsequently recognizing text in those regions. The vision task of recognizing text from the cropped regions is called Scene Text Recognition (STR).
STR makes it possible to read road signs, billboards, logos, and printed objects such as text on shirts, paper bills, etc. STR applications include practical use cases such as self-driving cars, augmented reality, retail analysis, education, devices for the visually impaired, and others.
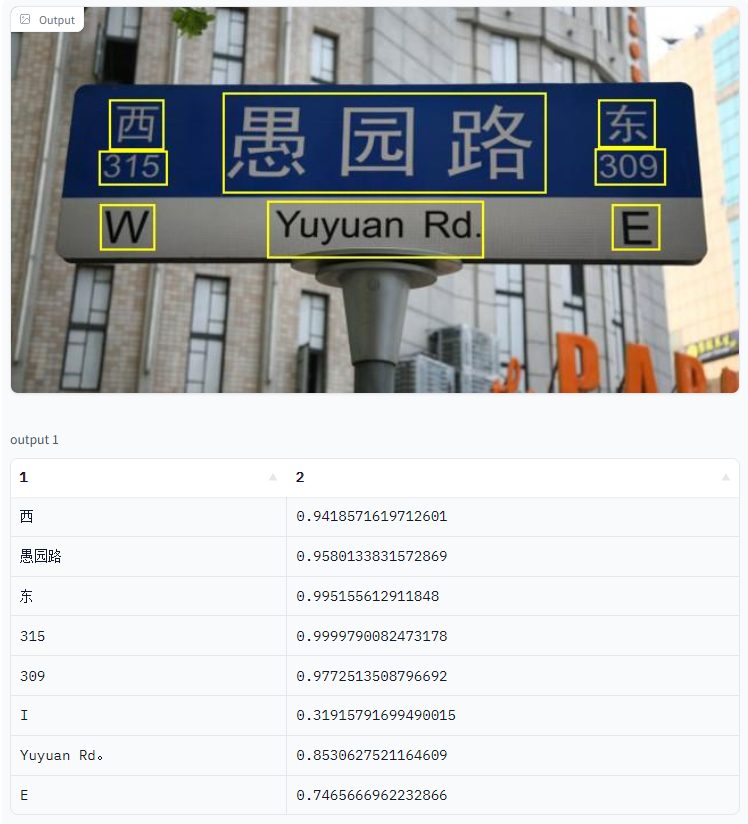
What is the Difference Between OCR and STR?
Comparing OCR with STR, optical character recognition is applicable where text attributes are provided in a uniform input form. Hence, STR can read text with varying font styles, text shapes, illumination, orientation, occlusion (partially hidden text), and inconsistent camera conditions.
In general, scene text recognition is required to read Text with AI algorithms in real-world scenarios that involve very challenging, natural environments with noisy, blurry, or distorted input images.
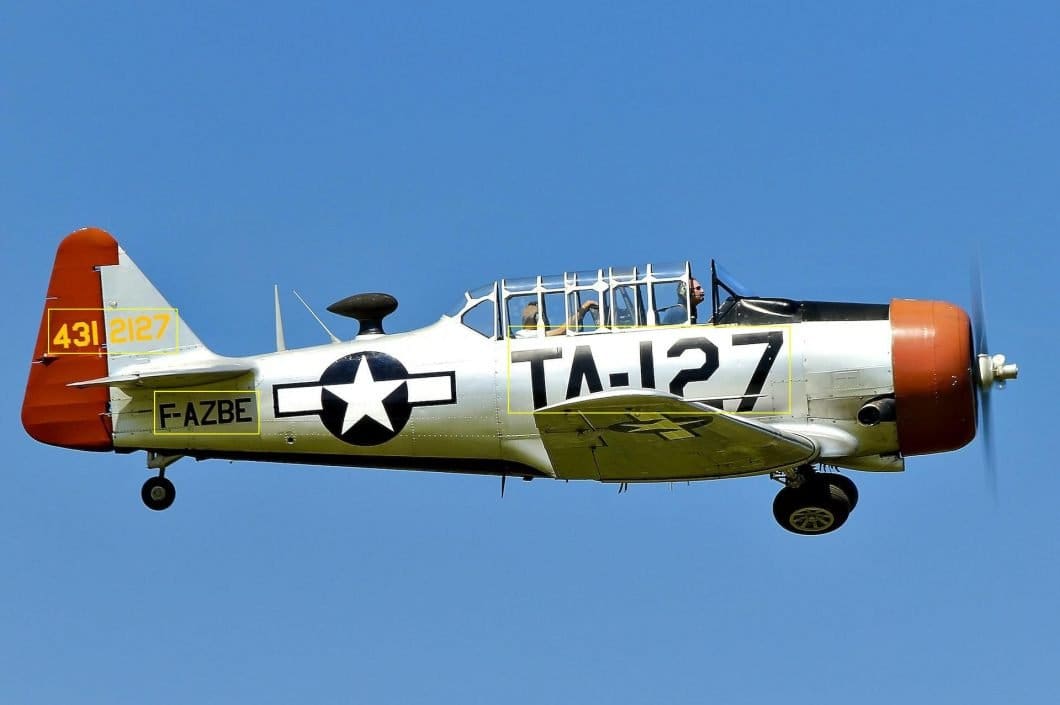

How does Optical Character Recognition work?
The concept of OCR is straightforward. However, its implementation can be quite challenging due to several factors, such as the variety of fonts or the methods used for letter formation. For example, an OCR implementation becomes exponentially more complex when non-digital handwriting samples are used as input instead of typed writing.
The entire process of OCR involves a series of steps that mainly contain three objectives: pre-processing of the image, character recognition, and post-processing of the specific output. Downstream tasks include Natural Language Processing (NLP) to not only read but also analyze and understand the meaning of text and speech.
OCR Demo Software for Testing
To see OCR software in action, we found a simple web demo software you can try to use: Text Extractor Tool by Brandfolder. This optical character recognition online tool can convert an image of text (such as a screenshot) into plaintext. Be sure to avoid uploading any sensitive images or photos containing personal identifying information.
For a more comprehensive demo, explore this image to Optical Character Recognition algorithm demo that allows Multilingual OCR, which works conveniently on all devices in multiple languages.

The Process of OCR Computer Vision
In the following, we will show how optical character recognition works and explain the main steps of traditional OCR technologies.
1. Scanning the Document
This is the prime step of OCR, which connects to a scanner to scan the document. Scanning the document decreases the number of variables to account for when creating the OCR software since it standardizes the inputs. Also, this step specifically enhances the efficiency of the entire process by ensuring perfect alignment and sizing of the specific document. This initial step can also include object detection, to focus subsequent vision-processing tasks on specific image areas.
2. Refining the Image
In this step, the optical character recognition software improves the elements of the document that need to be captured. Any imperfections, such as dust particles, are eliminated, and edges, as well as pixels, are smoothed to get a plain and clear text.
This step makes it easier for the program to capture manual data entry while being able to clearly “see” the words being inputted without, for instance, smudges or irregular dark areas. Such image processing tasks are essential in all types of vision pipelines, to sharpen or auto-brighten images. OpenCV provides a toolset that is often used for such tasks.
3. Binarization
The refined image document is then converted into a bi-level document image, containing only black and white colors, where black or dark areas are identified as characters. At the same time, white or light areas are identified as background.
This step aims to apply segmentation to the document to easily differentiate the foreground text from the background, which allows for the optimal recognition of characters.
4. Recognizing the Characters
In this step, the black areas are further processed to identify letters or digits. Usually, an OCR focuses on one character or block of text at a time. The recognition of characters is carried out by using one of the following two types of algorithms:
- Pattern recognition. The pattern recognition algorithm involves inserting text in different fonts and formats into the OCR software. The modified software is then used for comparing and recognizing the characters in the scanned document.
- Feature detection. Through the feature detection algorithm, the software applies rules considering the features of a certain letter or number to identify characters in the scanned document processing. Examples of features include the number of angled lines, crossed lines, or curves used for comparing and identifying characters. Such text recognition techniques are the basis of most deep learning OCR methods.
Simple OCR software compares the pixels of every scanned letter with an existing database to identify the closest match. However, sophisticated forms of OCR divide every character into its components, such as curves and corners, to compare and match physical features with corresponding letters.

5. Verifying the Accuracy
After the successful recognition of characters, the results are cross-referenced by utilizing the internal dictionaries of the OCR software to ensure accuracy. Measuring OCR accuracy is done by taking the output of an analysis conducted by an OCR and comparing it to the contents of the original version.
There are two typical methods for analyzing the accuracy of OCR software:
- Character-level accuracy, counting how many characters were detected correctly.
- Word-level accuracy, counting how many words were recognized correctly.
In most cases, 98-99% accuracy is the acceptable accuracy rate, measured at the page level (not algorithm level). This means that in a page of around 1,000 characters, 980-990 characters should be accurately identified by the OCR software.
The Best OCR Computer Vision Algorithm
Most Accurate OCR Algorithms
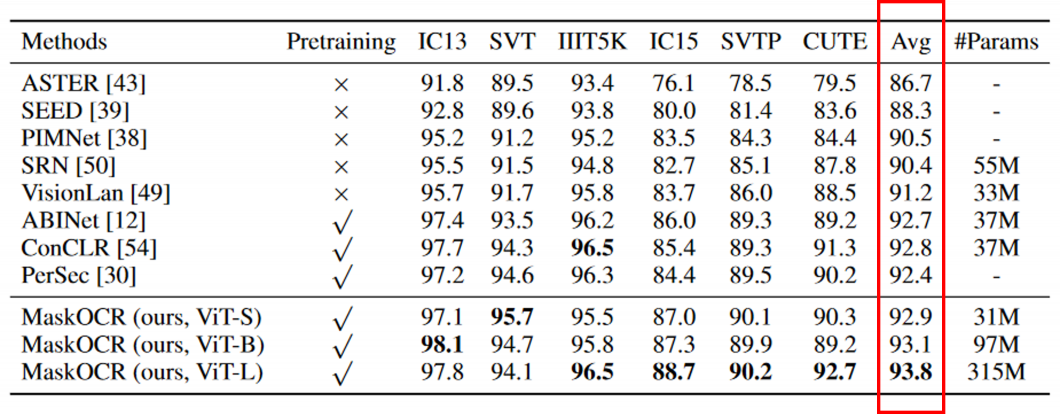
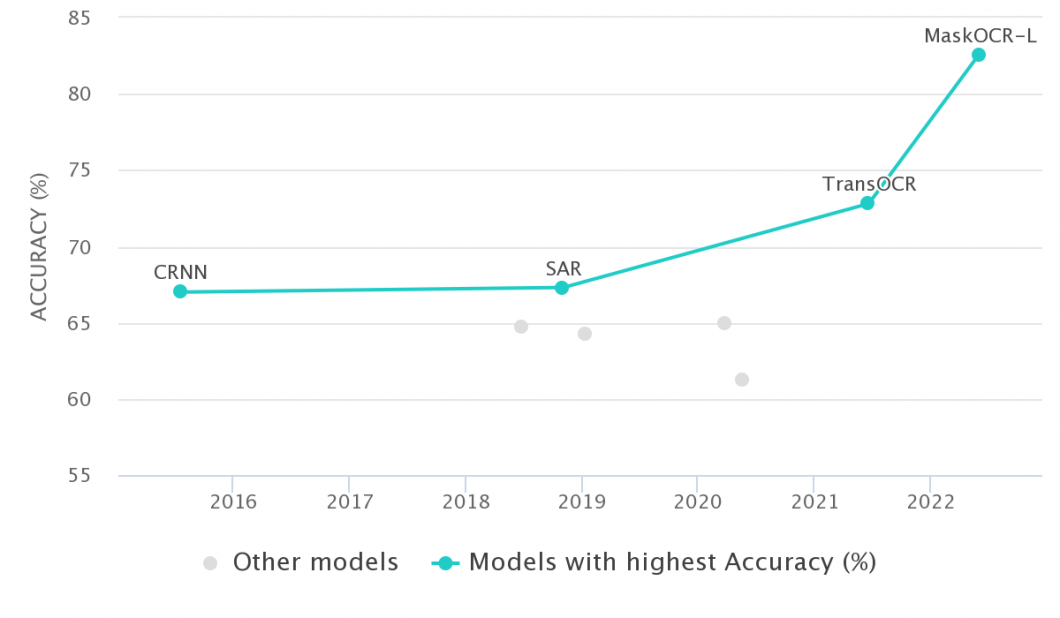
MaskOCR, which is based on Vision Transformers (ViT) and was released in June 2022, is the best-performing OCR algorithm and achieves superior results on benchmark datasets for both Chinese and English text images. The previous best algorithm for Optical Character Recognition on the Chinese BCTR dataset, TransOCR, was surpassed by MaskOCR.
The small model version of MaskOCR surpasses the previous best algorithm for Optical Character Recognition with comparable model sizes. Specifically, the Mask OCR method achieves better accuracy than PerSec, which is pre-trained with 100 million real data points, while it uses only 4.2 million real data points for pretraining.
ABINet and its extension ConCLR perform similarly to the small ViT version of MaskOCR, while MaskOCR pushes the state-of-the-art results to a new level of 93.8% accuracy.
Test the Algorithms Yourself
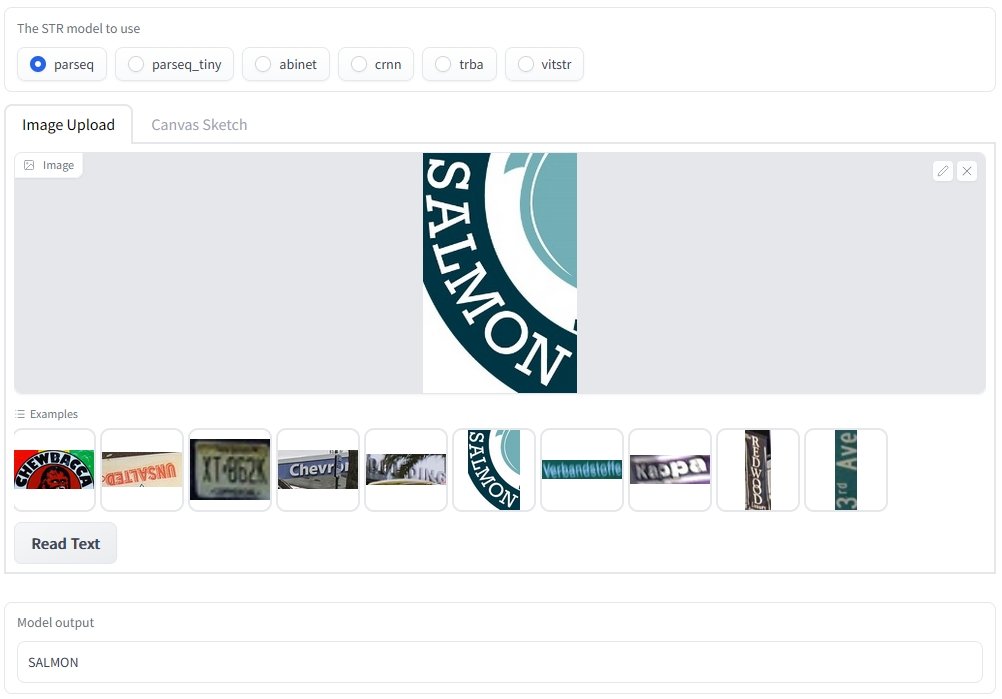
Use this interactive demo to test the PARSeq model, which achieves high-performing results in STR (Scene Text Recognition) benchmarks (91.9% accuracy) when trained using synthetic training data (more about data augmentation).
- Access the hosted OCR model here
- Select the OCR model to use
- Upload a text image or use a given example
- Click “Read Text.”
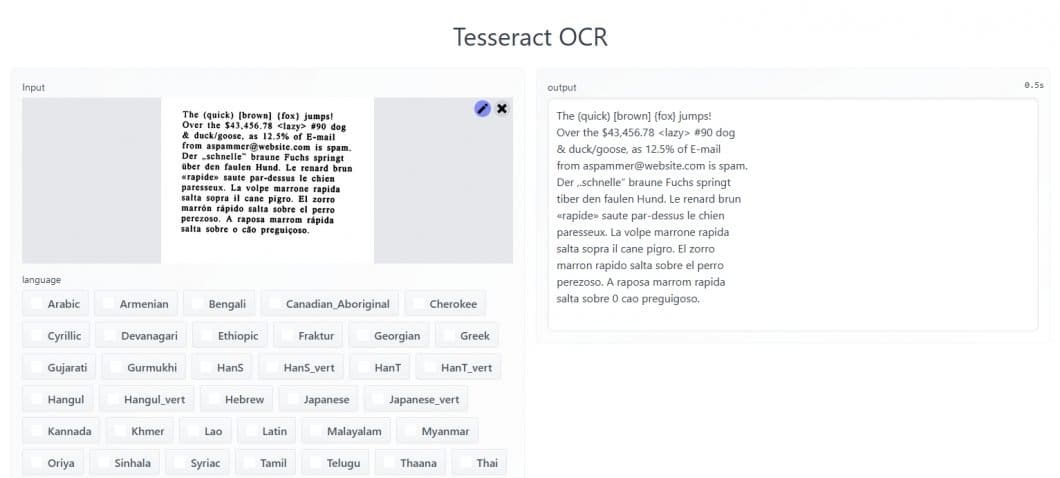
Tesseract Optical Character Recognition
What is Tesseract?
Tesseract is a character recognition engine that can read scanned text and convert it into digital text. It is open-source software that is released under the Apache License 2.0. Tesseract is available for various operating systems, including Windows, Linux, and Mac OS X.
Hence, Tesseract is a popular tool to recognize text in images, such as scanned paper documents and digital photos. Tesseract is accurate and efficient, and it can handle a variety of languages.
Tesseract OCR Software Demo for Testing
To recognize text in images with Tesseract, you input images that contain text. Tesseract can read a variety of image formats, including JPG, PNG, and TIFF.
OCR Computer Vision Use Cases
As everything becomes digitalized and advanced, enterprises use OCR software solutions to streamline business processes, improve accessibility, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Below, we list some of the best OCR solutions across industries today.
Number Plate Recognition with OCR
Automatic number-plate recognition (ANPR) uses OCR technology to identify the numbers on license plates. Today, number-plate recognition is used in a diverse set of commercial applications to find stolen cars, calculate fees for parking, invoice tolls or access control to safety zones, and more.

OCR Use Cases in Banking
The banking industry is one of the largest consumers of OCR recognition apps to enhance security, improve data management, optimize risk management, and enhance customer experience.
Before applying OCR technology, most banking documents were physical, including customer records, checks, bank statements, and others. Through the use of an OCR recognition solution, it becomes possible to digitize and store even older documents in databases.
This technology has also completely revolutionized the banking industry by:
- Providing easy verification: OCR allows a real-time verification of money deposit checks and a signature by scanning them using an OCR-based application. For example, users can digitally deposit and process checks with mobile banking apps, which process transactions within days through OCR-based check depositing features.
- Enhancing security: The electronic deposition of checks through OCR technology results in fraud prevention and increasingly secure transactions, fostering a better user experience. OCR can use the character reader count and machine learning methods to detect forged documents.
OCR Use Cases in Healthcare
OCR machine learning has proved to be beneficial for the healthcare industry. In the healthcare sector, OCR technology allows patient medical histories to be accessed digitally by patients and doctors alike.
In addition, patient records, including their X-rays, treatments, tests, hospital records, and insurance payments, can easily be scanned, searched, and stored using OCR full-form methods to digitize records and read labels with cameras.
Thus, OCR helps streamline the workflow and reduce manual work at hospitals while keeping the records up to date.
OCR Use Cases in Transportation
OCR technology has revolutionized the intelligent parking, intelligent character recognition (ICR), smart tolling, and transportation industries. Whether you’re booking a flight or a hotel, checking in to the airport or your hotel room, or managing your travel expenses, AI-based Optical Character Recognition solutions are useful at every point of contact to enhance customer experience in hotels and casinos.
When looking at the uses of computer vision in airports, many use mobile travel apps and machine learning OCR technology for automated data extraction in security and documentation applications. The applications of Optical Character Recognition tools range from scanning passports to storing personal data when booking a flight or a hotel.

Advantages Of Optical Character Recognition
Optical Character Recognition offers a wide range of benefits, many of which we reviewed in this article. However, we’ve listed the most important benefits of AI-based text recognition systems below.
- Improved accuracy: Software-based character recognition eliminates human errors, resulting in improved accuracy.
- Speed up the processes: The technology converts unstructured data into searchable information, making the required data available at faster rates and subsequently speeding up time-consuming business processes.
- Cost-effective: OCR technology does not require a lot of resources reducing the processing costs and the overall business costs.
- Enhanced customer satisfaction: The accessibility of searchable data by the customers ensures a good experience, assuring better customer satisfaction.
- Improved productivity: The easy accessibility of searchable data makes a stress-free environment for the employees, allowing them to focus on the main goals, boosting the productivity of a business.
What’s Next for OCR?
Optical character recognition turns scanned images and other visuals into text. This turns paper-based documents into editable and searchable digital mediums and for the development of an automated OCR system.
To deliver OCR in enterprise applications, check out Viso Suite, the end-to-end computer vision platform. Request a personalized demo here.
If you enjoyed this article, we suggest you read more about other applications of Computer Vision:
- Read our Guide to Image Recognition Technology
- Explore the Most Popular Computer Vision Applications
- Everything you need to know about Video Analytics
- AI in Sports and Computer Vision in Restaurants
